When Database Administrators manage multiple databases on
multiple servers, it is difficult to keep track of and monitor the used
percentage of data portion on every database. Though SQL Server has the capability
of auto growth whenever the data portion reaches 100%, it is always advisable
to increase the database size manually when it comes to VLDB. This article examines
monitoring the percentage used on the data portion of every database and alerting
the DBA using threshold settings. This article has been written for SQL Server
2000 server.
Step 1
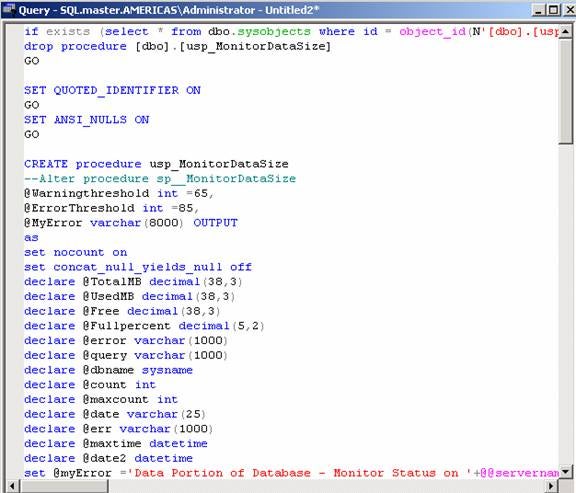
Create usp_MonitorDataSize
procedure on the server using the code below. [Refer Fig 1.0]
if exists (select * from dbo.sysobjects
where id =
object_id(N’[dbo].[usp_MonitorDataSize]’)
and OBJECTPROPERTY
(id, N’IsProcedure’) = 1)
drop procedure [dbo].[usp_MonitorDataSize]
GOSET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON
GO
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GOCREATE procedure usp_MonitorDataSize
–Alter procedure sp__MonitorDataSize
@Warningthreshold int =65,
@ErrorThreshold int =85,
@MyError varchar(8000) OUTPUT
as
set nocount on
set concat_null_yields_null off
declare @TotalMB decimal(38,3)
declare @UsedMB decimal(38,3)
declare @Free decimal(38,3)
declare @Fullpercent decimal(5,2)
declare @error varchar(1000)
declare @query varchar(1000)
declare @dbname sysname
declare @count int
declare @maxcount int
declare @date varchar(25)
declare @err varchar(1000)
declare @maxtime datetime
declare @date2 datetime
set @myError =’Data Portion of Database – Monitor Status on ‘+@@servername + char(13)
set @myError =@myError +’_________________________________________’ + char(13)
set @date2=getdate()
set @date = convert(varchar(100), @date2,109)create table #dbtable (id int identity(1,1), dbname varchar(256))
insert into #dbtable (dbname) select name from master..sysdatabases
where –name !=’tempdb’ and
status & 32 != 32
and status & 64 != 64 and status & 128 != 128
and status & 256 != 256 and status & 512 != 512
and status & 1024 != 1024 and status & 4096 != 4096
and status & 32768 !=32768
order by name
set @count=1
set @maxcount = (select max(id) from #dbtable)create table #MDFtable(dbname varchar(256) , Fileid int, FileGroup int,
Totalextents decimal(38,3),UsedExtents decimal(38,3),LogicalName
varchar(256),Filename varchar(1200), totalmb as
(TotalExtents*64.000)/1024.000 ,usedmb as (Usedextents*64.000)/1024.000
,free as ((TotalExtents*64.000*1.000) –
(Usedextents*64.000*1.000))/1024.000,freepercent as
(((TotalExtents*64.000*1.000) –
(Usedextents*64.000*1.000))/(TotalExtents*64.000*1.000))*100)
create table #MDFtable3(id int identity(1,1),
dbname varchar(256),
TotalMB decimal(38,3),
UsedMB decimal(38,3),
Free as (TotalMB*1.000)-(UsedMB*1.000),
Fullpercent as 100.000-(((TotalMB*1.000)-(UsedMB*1.000))/(TotalMB*1.000))*100.000)While @count <= @maxcount
begin
truncate table #MDFtable
set @dbname = (select dbname from #dbtable where id = @count)set @query =’Begin use [’+ @dbname + ‘] end begin DBCC showfilestats with NO_INFOMSGS end’
insert #MDFtable
(Fileid,FileGroup,Totalextents,UsedExtents,LogicalName,Filename) exec
(@query)update #MDFtable set dbname =@dbname –where dbname is null
insert #MDFtable3(dbname,TotalMB,UsedMB)
select @dbname,sum(TotalMB) ,sum(UsedMB) from #MDFtable group by dbnameset @count = @count+1
end
drop table #MDFtable
drop table #dbtable
set @maxcount = (select max(id) from #MDFtable3)
set @count=1
While @count <= @maxcount
beginSelect @dbname=dbname,@TotalMB=TotalMB,@UsedMB=UsedMB,@Free=free,
@Fullpercent=fullpercent
from #MDFtable3 where id = @countif @Fullpercent>@ErrorThreshold
begin
set @error = ‘Warning {Severe}= Data portion of database exeeded the threshold. :
Database=’ +@dbname +’:
TotalMB=’+convert(varchar(30),@totalmb)+’:
UsedMB=’+convert(varchar(30),@Usedmb)+’:
Free=’+convert(varchar(30),@free)+’:
Percentage Full=’+convert(varchar(30),@fullpercent)+’%:
WarningThreshold=’+convert(varchar(30),@Warningthreshold)+’%:
ErrorThreshold=’+convert(varchar(30),@Errorthreshold)+’%:
Date=’+@date
end
else
begin
if @Fullpercent>@Warningthreshold
begin
set @error = ‘Warning = Data portion of database exeeded the threshold.
Database=’ +@dbname ++’:
TotalMB=’+convert(varchar(30),@totalmb)+’:
UsedMB=’+convert(varchar(30),@Usedmb)+’:
Free=’+convert(varchar(30),@free)+’:
Percentage Full=’+convert(varchar(30),@fullpercent)+’%:
WarningThreshold=’+convert(varchar(30),@Warningthreshold)+’%:
ErrorThreshold=’+convert(varchar(30),@Errorthreshold)+’%:
Date=’+@date
end
else
begin
set @error = ‘Data Size Information: Database=’ +@dbname ++’:
TotalMB=’+convert(varchar(30),@totalmb)+’:
UsedMB=’+convert(varchar(30),@Usedmb)+’:
Free=’+convert(varchar(30),@free)+’:
Percentage Full=’+convert(varchar(30),@fullpercent)+’%:
WarningThreshold=’+convert(varchar(30),@Warningthreshold)+’%:
ErrorThreshold=’+convert(varchar(30),@Errorthreshold)+’%:
Date=’+@date
end
endset @myerror=@myerror+char(13)+ @error
set @count=@count+1
enddrop table #MDFtable3
print @myerror
GO
SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER OFF
GO
SET ANSI_NULLS ON
GO
Download
usp_MonitorDataSize.sql.
[Fig 1.0]
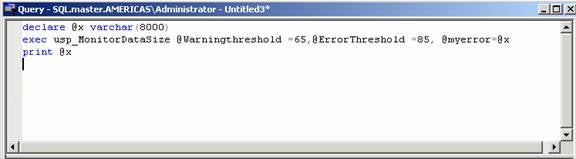
Step 2
Execute
the above procedure as shown below. [Refer Fig 1.1]
declare @x varchar(8000)
exec usp_MonitorDataSize @Warningthreshold =65,@ErrorThreshold =85, @myerror=@x
print @x
[Fig 1.1]
Note: Please update the warning
threshold and Error threshold to suit your requirement.
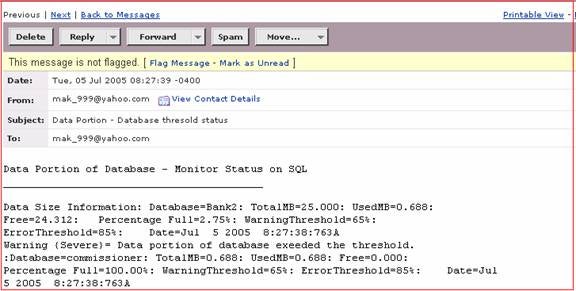
You will see
three kinds of the results from the procedure, as shown below. [Fig 1.2]
When the
data portion exceeds the warning threshold then the result looks like this:
Warning = Data portion of database exeeded the
threshold. Database=Northwind: TotalMB=4.438: UsedMB=3.063: Free=1.375:
Percentage Full=69.02%: WarningThreshold=65%: ErrorThreshold=85%: Date=Jul
5 2005 7:56:25:230A
When the
data portion exceeds the error threshold then the result looks like this:
Warning {Severe}= Data portion of database exeeded the
threshold. :Database=Workstation_Reboot: TotalMB=0.688: UsedMB=0.688:
Free=0.000: Percentage Full=100.00%: WarningThreshold=65%: ErrorThreshold=85%:
Date=Jul 5 2005 7:56:25:230A
When the
data portion does not exceed the error threshold or the warning threshold then
the result looks like this:
Data Size Information: Database=tempdb: TotalMB=36.000: UsedMB=0.750:
Free=35.250: Percentage Full=2.08%: WarningThreshold=65%: ErrorThreshold=85%:
Date=Jul 5 2005 7:56:25:230A
[Fig 1.2]
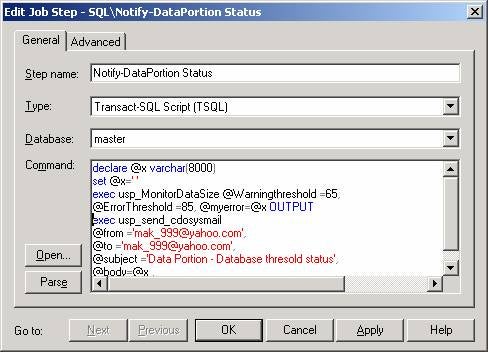
Step 3
Schedule
this procedure using SQL Server Job Scheduler as shown below. [Refer Fig 1.3,
Fig 1.4 and Fig 1.5]
declare @x varchar(8000)
set @x=’ ‘
exec usp_MonitorDataSize @Warningthreshold =65,@ErrorThreshold =85, @myerror=@x OUTPUTexec usp_send_cdosysmail
@from =’mak_999@yahoo.com’,
@to =’mak_999@yahoo.com’,
@subject =’Data Portion – Database thresold status’,
@body=@x ,
@smtpserver =’mail.optonline.net’,
@bodytype = ‘textbody’
Note: Please update the SMTP
server name, From email address and To email to suit your
environment.
[Fig 1.3]
[Fig 1.4]
[Fig 1.5]
Since the
result of the procedure is stored in an OUTPUT variable, you can use any kind
of email procedure for notification. If you are planning to use usp_send_cdosysmail
please refer my article, "Formatted
emails from SQL Server." You can also use SQL Mail xp_sendmail to send this result as
email. [Refer Fig 1.6]
[Fig 1.6]
Conclusion
As
mentioned, this article illustrates how to monitor the percentage used on the
data portion of the database, so that the DBA can increase the database size as
and when necessary, especially when it is VLDB.