Welcome to the fourth article in
my series SQL Server Administration in 15 Minutes a Week. Up
to this point the series has focused on options,
requirements, and the installation process. This week we
will start working with the tools provided with SQL Server
2000. The topics for this article include:
– Navigating Enterprise Manager
– SQL Server Groups
– Modifying SQL Server Registrations
– Adding SQL Server Registrations
– System Databases
– Books Online
Navigating Enterprise Manager
The Enterprise Manager is a graphical interface tool used to
administer your SQL Servers. You can use the Enterprise
Manager to configure SQL Server options, create/edit/view
databases, perform maintenance and backups, and do quite a
few more tasks that we will look at over the next few weeks.
Back a couple of articles we saw that the SQL Server 2000
setup creates a program group on the Start Menu named
“Microsoft SQL Server.” To launch the Enterprise Manager
Click Start > Programs > Microsoft SQL Server > Enterprise
Manager
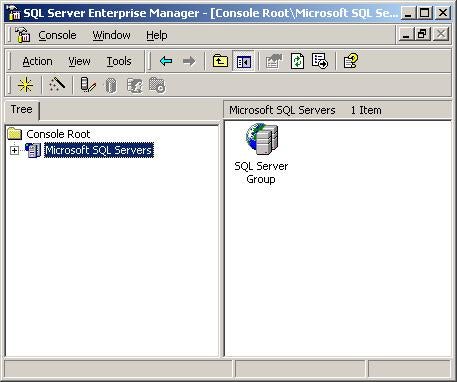
If you have ever used the Microsoft Management Console (MMC)
you will notice that the Enterprise Manager looks familiar.
This is because the Enterprise Manager is a MMC snap-in like
many of the tools provided with Windows 2000. If you would
like more information on using the Microsoft Management
Console have a look at the following link:
http://www.microsoft.com/windows2000/techinfo/howitworks/management/mmcover.asp
By expanding “Microsoft SQL Server” and then expanding “SQL
Server Group” you can locate the SQL Server you have
installed on your local system. Expanding the tree further
allows you to manage databases, security, replication, etc.
Right clicking the SQL Servers
icon in the tree view will also popup a menu with options
that allows you to start/stop the server, view the server
messages, access the server’s properties, etc.
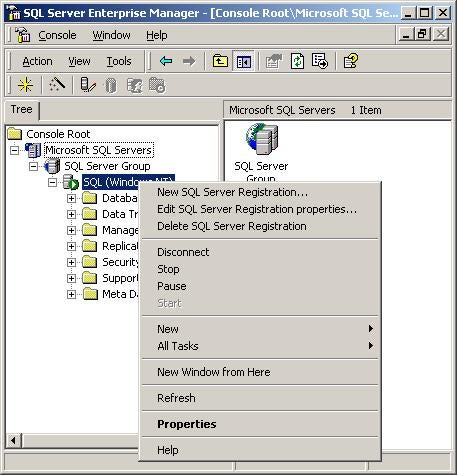
Enterprise Manager also provides you with a quick look at
the status of your SQL Servers. Depending on the icon
displayed in the tree view you can tell if SQL Server is
running, stopped, paused, or if you are currently connected
to the server. Use the following table to check the status
of your SQL Servers:
|
|
Server Running, You are currently connected |
|
|
Server Running, You are not currently connected |
|
|
Server Paused |
|
|
Server Stopped |
SQL Server Groups and Registrations
In many cases you will want to reorganize how your SQL Servers (or Instances)
are listed in Enterprise Manager. To make organizing your
SQL Servers simpler, Enterprise Manager allows you to create
Server Groups. Creating a new group is not complicated; start
by right clicking “Microsoft SQL Server” on the Enterprise
Manager tree.
Select “New SQL Server Group” from the popup menu.
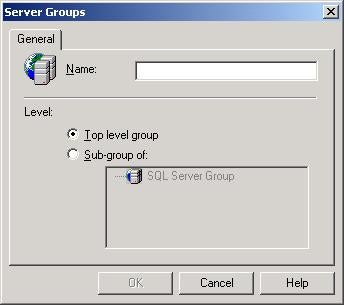
The Server Groups screen allows you to create new groups as
Top level (under “Microsoft SQL Server”) or as a Sub-group
under an existing group.
Enter a name for the group in the “Name:” textbox and click
OK.
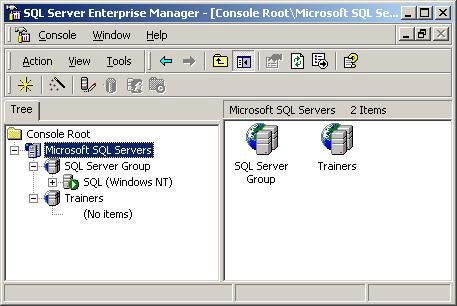
You can continue to add Groups and Sub-groups until you have
the ideal layout for your organization.
»
See All Articles by Columnist Michael Aubert


